Conditional Types I & II
Conditional Types
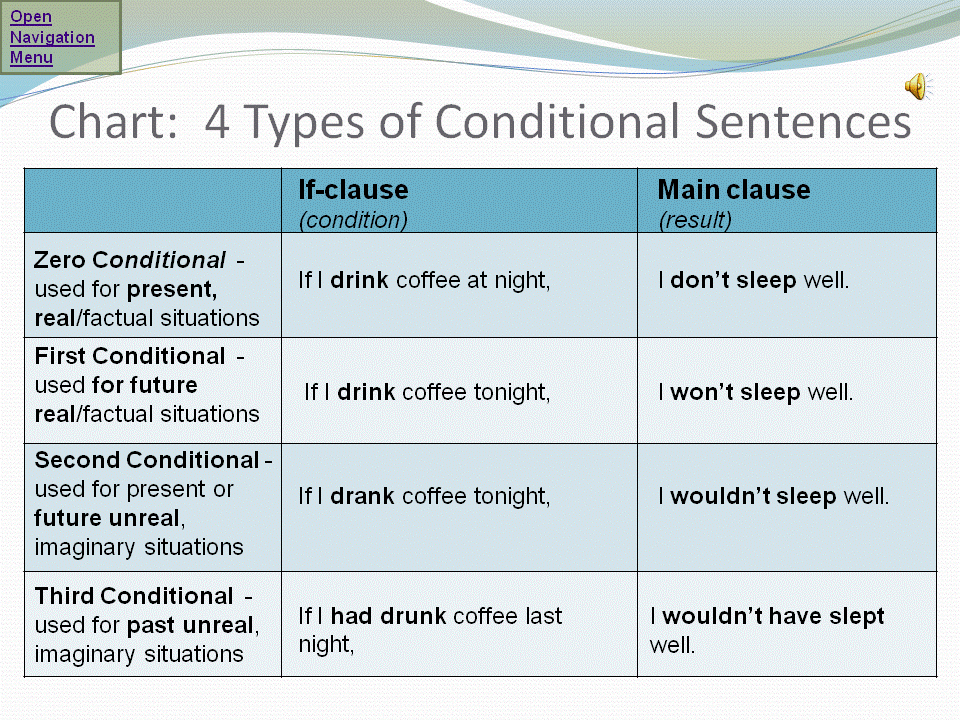
The conditional sentence in English can be seen in terms of three principal types.
Type I
We use this type to imply that it is possible that the action in the if-clause will be performed. This kind is structured as follows:
If-clause
|
main clause
|
Verb in the present tense
| Verb in the future tense |
If you work hard,
| you will succeed. |
It is still probable that you will succeed if the condition (to work hard) is fulfilled.
N.B. The verb in the if-clause is never in the future.
N.B. The verb in the if-clause is never in the future.
If you go to the United States, you will be able to practise your English.
If Barcelonaloses another match, they will say farewell to the Spanish League.
We won’t be on time for the meeting if we keep on walking slowly.
This type however is used to indicate that the idea is improbable or unreal. The result of the condition is imaginary. It is structured as follows:
If-clause
|
main clause
|
Simple past tense (subjunctive)
| conditional tense (would do etc.) |
If she had wings,
| she would fly. |
Situations :
– Roger doesn’t speak Spanish; so, he can’t communicate with the English people inLondon.
If Roger spoke Spanish, he would be able to communicate with the English people inLondon.
B- Derek is only 17. So, he isn’t allowed to drive a car.
If Derek were older, he would be allowed to drive a car.
C- Bashar Al Assad doesn’t have enough courage. He can’t step down.
If Bachar Al Assad had enough courage, he would step down.
Omar Ait Hnizzi – Lycée IbnBattouta/Aklim
Cliquer sur l'image pour l'agrandir